2022 NAB Broadcast Engineering and Information Technology (BEIT) Conference
April 24-26, 2022 | Las Vegas, US
Vignesh V Menon (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Hadi Amirpour (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Christian Feldmann (Bitmovin, Klagenfurt),
Adithyan Ilangovan (Bitmovin, Klagenfurt), Martin Smole (Bitmovin, Klagenfurt), Mohammad Ghanbari (School of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, University of Essex, Colchester, UK), and Christian Timmerer (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt).
Abstract:
Current per-title encoding schemes encode the same video content at various bitrates and spatial resolutions to find optimal bitrate-resolution pairs (known as bitrate ladder) for each video content in Video on Demand (VoD) applications. But in live streaming applications, a fixed bitrate ladder is used for simplicity and efficiency to avoid the additional latency to find the optimized bitrate-resolution pairs for every video content. However, an optimized bitrate ladder may result in (i) decreased storage or network resources or/and (ii) increased Quality of Experience (QoE). In this paper, a fast and efficient per-title encoding scheme (Live-PSTR) is proposed tailor-made for live Ultra High Definition (UHD) High Framerate (HFR) streaming. It includes a pre-processing step in which Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)-energy-based low-complexity spatial and temporal features are used to determine the complexity of each video segment, based on which the optimized encoding resolution and framerate for streaming at every target bitrate is determined. Experimental results show that, on average, Live-PSTR yields bitrate savings of 9.46% and 11.99% to maintain the same PSNR and VMAF scores, respectively compared to the HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) bitrate ladder.
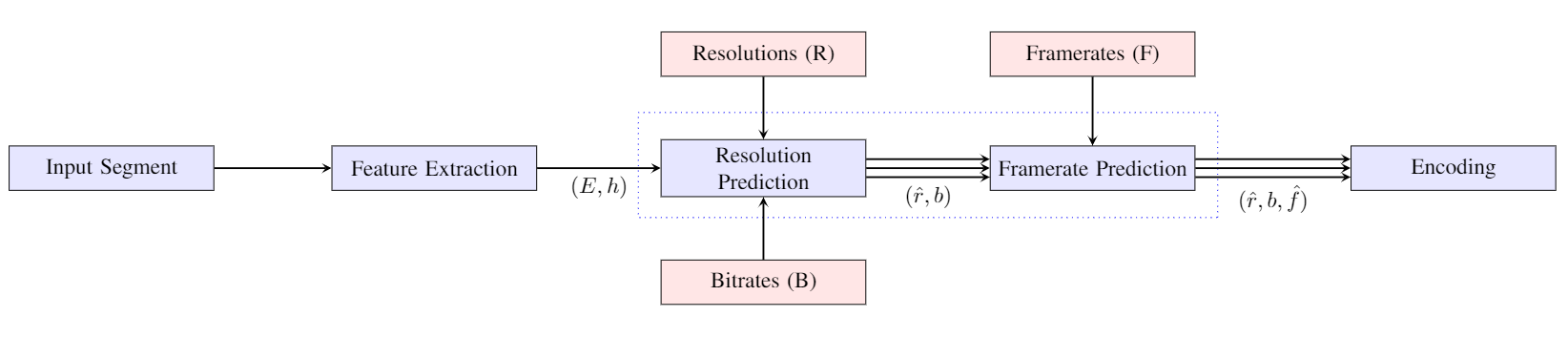
Architecture of Live-PSTR