In Carinthia, researchers find an open test laboratory in the 5G Playground Carinthia, where the possibilities of the new mobile phone technology can be explored. The problem is: 5G enables the fast transmission of large amounts of data, but these also have to be processed. Read the whole interview of Univ.-Prof. DI Dr. Radu Prodan in the latest University Klagenfurt news.
On Tuesday the 25th of January 2022, Hadi Amirpour successfully defended his Ph.D. thesis under supervision of Assoc.-Prof. DI Dr. Christian Timmerer and Assoc.-Prof. Dr. Klaus Schöffmann. The defense was chaired by Assoc.-Prof. DI Dr. Mathias Lux and the examiners were Emeritus Prof. Dr. Mohammad Ghanbari (University of Essex, UK) and Univ.-Prof. DI Dr. Hermann Hellwagner (University of Klagenfurt).
We are pleased to congratulate Dr. Hadi Amirpour on passing his Ph.D. exam!
The project “CardioHPC” (CardioHPC Improving DL-based Arrhythmia Classification Algorithm and Simulation of Real-Time Heart Monitoring of Thousands of Patients) has been accepted in the “First call for FF4EuroHPC application experiments” (funded under the European Community’s Horizon 2020 Programme). Prof. Prodan will take over the project management in Klagenfurt.
The goal is to conduct an experiment to improve our DL-based arrhythmia classification algorithm and conduct a large-scale demonstration experiment to simulate a monitoring center for automated monitoring and alerting for 10K patients through HPC, focusing on quality and identifying HPC as a key tool for innovation.
Project Partners: The University of Stuttgart, Innovation Dooel, University in Skopje
Project duration: 15 months
2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)
May 22-27, 2022 | Singapore
Conference Website
Vignesh V Menon (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Hadi Amirpour (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Mohammad Ghanbari (School of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, University of Essex, Colchester, UK), and Christian Timmerer (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt).
Abstract:
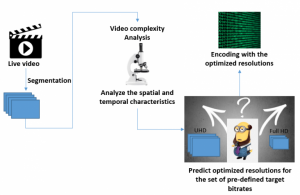
Current per-title encoding schemes encode the same video content at various bitrates and spatial resolutions to find an optimal bitrate ladder for each video content in Video on Demand (VoD) applications. However, in live streaming applications, a fixed resolution-bitrate ladder is used to avoid the additional encoding time complexity to find optimum resolution-bitrate pairs for every video content. This paper introduces an online per-title encoding scheme (OPTE) for live video streaming applications. In this scheme, each target bitrate’s optimal resolution is predicted from any pre-defined set of resolutions using Discrete Cosine Transform(DCT)-energy-based low-complexity spatial and temporal features for each video segment. Experimental results show that, on average, OPTE yields bitrate savings of 20.45% and 28.45% to maintain the same PSNR and VMAF, respectively, compared to a fixed bitrate ladder scheme (as adopted in current live streaming deployments) without any noticeable additional latency in streaming.
Keywords:
Per-title encoding, live streaming, bitrate ladder, convex-hull prediction
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
Farzad Tashtarian (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Abdelhak Bentaleb (National University of Singapore), Alireza Erfanian (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Hermann Hellwagner (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Christian Timmerer (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), and Roger Zimmermann (National University of Singapore).
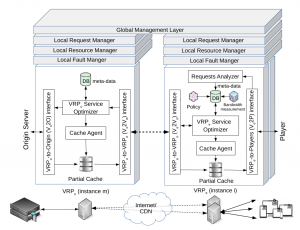 Abstract: While most of the HTTP adaptive streaming (HAS) traffic continues to be video-on-demand (VoD), more users have started generating and delivering live streams with high quality through popular online streaming platforms. Typically, the video contents are generated by streamers and being watched by large audiences which are geographically distributed far away from the streamers’ locations.
Abstract: While most of the HTTP adaptive streaming (HAS) traffic continues to be video-on-demand (VoD), more users have started generating and delivering live streams with high quality through popular online streaming platforms. Typically, the video contents are generated by streamers and being watched by large audiences which are geographically distributed far away from the streamers’ locations.
The locations of streamers and audiences create a significant challenge in delivering HAS-based live streams with low latency and high quality. Any problem in the delivery paths will result in a reduced viewer experience. In this paper, we propose HxL3, a novel architecture for low-latency live streaming. HxL3 is agnostic to the protocol and codecs that can work equally with existing HAS-based approaches. By holding the minimum number of live media segments through efficient caching and prefetching policies at the edge, improved transmissions, as well as transcoding capabilities, HxL3 is able to achieve high viewer experiences across the Internet by alleviating rebuffering and substantially reducing initial startup delay and live stream latency. HxL3 can be easily deployed and used. Its performance has been evaluated using real live stream sources and entities that are distributed worldwide. Experimental results show the superiority of the proposed architecture and give good insights into how low latency live streaming is working.
Index Terms—Live streaming, HAS, DASH, HLS, CMAF, edge computing, low latency, caching, prefetching, transcoding.
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC)
May 16–20, 2022 | Seoul, South Korea
Reza Farahani (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Farzad Tashtarian (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Christian Timmerer (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Mohammad Ghanbari (School of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, University of Essex, Colchester, UK), and Hermann Hellwagner (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt).
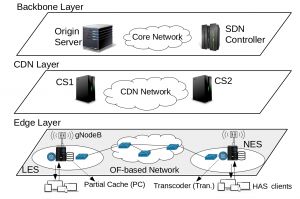 Abstract: With the emerging demands of high-definition and low-latency video streams, HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS) is considered the principal video delivery technology over the Internet. Network-assisted video streaming schemes, which employ modern networking paradigms, e.g., Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Network Function Virtualization (NFV), and edge computing, have been introduced as promising complementary solutions in the HAS context to improve users’ Quality of Experience (QoE) as well as network utilization. However, the existing network-assisted HAS schemes have not fully used edge collaboration techniques and SDN capabilities for achieving the aforementioned aims. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces a coLlaborative Edge- and SDN-Assisted framework for HTTP aDaptive vidEo stReaming (LEADER). In LEADER, the SDN controller collects various information items and runs a central optimization model that minimizes the HAS clients’ serving time, subject to the network’s and edge servers’ resource constraints. Due to the NP-completeness and impractical overheads of the central optimization model, we propose an online distributed lightweight heuristic approach consisting of two phases that runs over the SDN controller and edge servers, respectively. We implement the proposed framework, conduct our experiments on a large-scale testbed including 250 HAS players, and compare its effectiveness with other strategies. The experimental results demonstrate that LEADER outperforms baseline schemes in terms of both users’ QoE and network utilization, by at least 22% and 13%, respectively.
Abstract: With the emerging demands of high-definition and low-latency video streams, HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS) is considered the principal video delivery technology over the Internet. Network-assisted video streaming schemes, which employ modern networking paradigms, e.g., Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Network Function Virtualization (NFV), and edge computing, have been introduced as promising complementary solutions in the HAS context to improve users’ Quality of Experience (QoE) as well as network utilization. However, the existing network-assisted HAS schemes have not fully used edge collaboration techniques and SDN capabilities for achieving the aforementioned aims. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces a coLlaborative Edge- and SDN-Assisted framework for HTTP aDaptive vidEo stReaming (LEADER). In LEADER, the SDN controller collects various information items and runs a central optimization model that minimizes the HAS clients’ serving time, subject to the network’s and edge servers’ resource constraints. Due to the NP-completeness and impractical overheads of the central optimization model, we propose an online distributed lightweight heuristic approach consisting of two phases that runs over the SDN controller and edge servers, respectively. We implement the proposed framework, conduct our experiments on a large-scale testbed including 250 HAS players, and compare its effectiveness with other strategies. The experimental results demonstrate that LEADER outperforms baseline schemes in terms of both users’ QoE and network utilization, by at least 22% and 13%, respectively.
Keywords:
Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH), Network-Assisted Video Streaming, Video Transcoding, Quality of Experience (QoE), Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Network Function Virtualization (NFV), Edge Computing, Edge Collaboration
Data Compression Conference (DCC)
March 22-25, 2022 | Snowbird, Utah, US
Conference Website
Vignesh V Menon (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Hadi Amirpour (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Mohammad Ghanbari (School of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, University of Essex, Colchester, UK), and Christian Timmerer (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt).
Abstract:
High Framerate (HFR) video streaming enhances the viewing experience and improves visual clarity. However, it may lead to an increase of both encoding time complexity and compression artifacts at lower bitrates. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a content-aware frame dropping algorithm (CODA) to drop frames uniformly in every video (segment) according to the target bitrate and the video characteristics. The algorithm uses Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)-energy-based low-complexity spatial and temporal features to determine the video properties and then predict the optimized framerate, yielding the highest compression efficiency. The effectiveness of CODA is evaluated with High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) bitstreams based on the x265 HEVC open-source encoder. Experimental results show that, on average, CODA reduces the overall Ultra High Definition (UHD) encoding time by 21.82% with bit-rate savings of 15.87% and 18.20% to maintain the same PSNR and VMAF scores, respectively compared to the original frame-rate encoding.
Title: Decentralized Machine Learning for Intelligent Health Care Systems on the Computing Continuum
Authors: Dragi Kimovski, Sasko Ristov, Radu Prodan
Abstract: The introduction of electronic personal health records (EHR) enables nationwide information exchange and curation among different health care systems. However, the current EHR systems do not provide transparent means for diagnosis support, medical research, or can utilize the omnipresent data produced by the personal medical devices. Besides, the EHR systems are centrally orchestrated, which could potentially lead to a single point of failure. Therefore, in this article, we explore novel approaches for decentralizing machine learning over distributed ledgers to create intelligent EHR systems that can utilize information from personal medical devices for improved knowledge extraction. Consequently, we proposed and evaluated a conceptual EHR to enable anonymous predictive analysis across multiple medical institutions. The evaluation results indicate that the decentralized EHR can be deployed over the computing continuum with reduced machine learning time of up to 60% and consensus latency of below 8 seconds.
The 5th Klagenfurt Winter Game Jam took place as a hybrid event on Dec 17-19, 2021. Over 100 participants teamed up over the weekend to create altogether 26 games on the topic of “What’s in the box?”.
The games can be found and played at https://itch.io/jam/5th-winter-game-jam.

In a hybrid (i.e. online and offline) attendance mode at the project meeting in Ohrid, Macedonia, the ARTICONF team gave a final push to have a unified and integrated ARTICONF toolset for DApp developers. The consortium led by project coordinator Prof. Prodan also outlined a detailed action plan for the remaining six months with regards to exploitation and dissemination of ARTICONF’s latest results and developed technologies.