IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management
Authors: Reza Farahani, Ekrem Cetinkaya, Christian Timmerer, Mohammad Shojafar, Mohammad Ghanbari, and Hermann Hellwagner
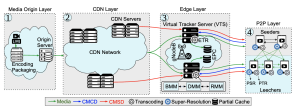
Abstract: Recent years have witnessed video streaming demands evolve into one of the most popular Internet applications. With the ever-increasing personalized demands for high-definition and low-latency video streaming services, network-assisted video streaming schemes employing modern networking paradigms have become a promising complementary solution in the HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS) context. The emergence of such techniques addresses long-standing challenges of enhancing users’ Quality of Experience (QoE), end-to-end (E2E) latency, as well as network utilization. However, designing a cost-effective, scalable, and flexible network-assisted video streaming architecture that supports the aforementioned requirements for live streaming services is still an open challenge. This article leverage novel networking paradigms, i.e., edge computing and Network Function Virtualization (NFV), and promising video solutions, i.e., HAS, Video Super-Resolution (SR), and Distributed Video Transcoding (TR), to introduce A Latency- and cost-aware hybrId P2P-CDN framework for liVe video strEaming (ALIVE). We first introduce the ALIVE multi-layer architecture and design an action tree that considers all feasible resources (i.e., storage, computation, and bandwidth) provided by peers, edge, and CDN servers for serving peer requests with acceptable latency and quality. We then formulate the problem as a Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) optimization model executed at the edge of the network. To alleviate the optimization model’s high time complexity, we propose a lightweight heuristic, namely, Greedy-Based Algorithm (GBA). Finally, we (i) design and instantiate a large-scale cloud-based testbed including 350 HAS players, (ii) deploy ALIVE on it, and (iii) conduct a series of experiments to evaluate the performance of ALIVE in various scenarios. Experimental results indicate that ALIVE (i) improves the users’ QoE by at least 22%, (ii) decreases incurred cost of the streaming service provider by at least 34%, (iii) shortens clients’ serving latency by at least 40%, (iv) enhances edge server energy consumption by at least 31%, and (v) reduces backhaul bandwidth usage by at least 24% compared to baseline approaches.
Keywords: HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS); Edge Com- puting; Network Function Virtualization (NFV); Content Deliv- ery Network (CDN); Peer-to-Peer (P2P); Quality of Experience (QoE); Video Transcoding; Video Super-Resolution.