Authors: Ahmed Telili (TII, UAE), Wassim Hamidouche (TII, UAE), Brahim Farhat (TII, UAE), Hadi Amirpour (AAU, Austria), Christian Timmerer (AAU, Austria), Ibrahim Khadraoui (TII, UAE), Jiajie Lu (Politecnico di Milano, Italy), The Van Le (IVCL, South Korea), Jeonneung Baek (IVCL, South Korea), Jin Young Lee (IVCL, South Korea), Yiying Wei (AAU, Austria), Xiaopeng Sun (Meituan Inc. China), Yu Gao (Meituan Inc. China), JianCheng Huang (Meituan Inc. China) and Yujie Zhong (Meituan Inc. China)
Journal: Signal Processing: Image Communication
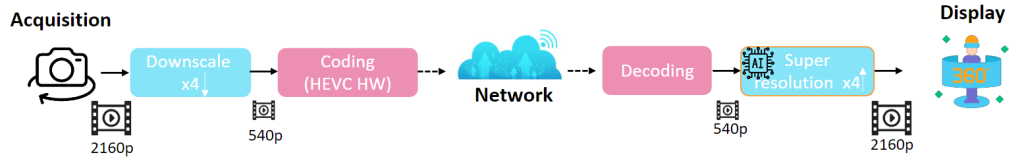
Abstract: Omnidirectional (360-degree) video is rapidly gaining popularity due to advancements in immersive technologies like virtual reality (VR) and extended reality (XR). However, real-time streaming of such videos, particularly in live mobile scenarios such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), is hindered by limited bandwidth and strict latency constraints. While traditional methods such as compression and adaptive resolution are helpful, they often compromise video quality and introduce artifacts that diminish the viewer’s experience. Additionally, the unique spherical geometry of 360-degree video, with its wide field of view, presents challenges not encountered in traditional 2D video. To address these challenges, we initiated the 360-degree Video Super Resolution and Quality Enhancement challenge. This competition encourages participants to develop efficient machine learning (ML)-powered solutions to enhance the quality of low-bitrate compressed 360-degree videos, under two tracks focusing on 2× and 4× super-resolution (SR). In this paper, we outline the challenge framework, detailing the two competition tracks and highlighting the SR solutions proposed by the top-performing models. We assess these models within a unified framework, (i) considering quality enhancement, (ii) bitrate gain, and (iii) computational efficiency. Our findings show that lightweight single-frame models can effectively balance visual quality and runtime performance under constrained conditions, setting strong baselines for future research. These insights offer practical guidance for advancing real-time 360-degree video streaming, particularly in bandwidth-limited immersive applications.