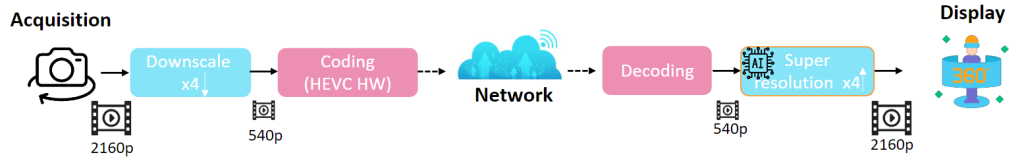
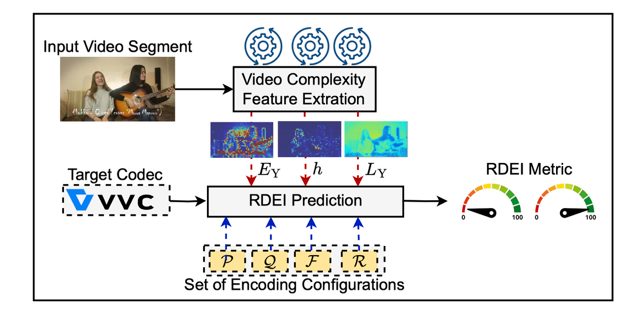
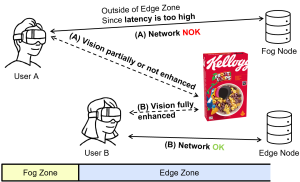
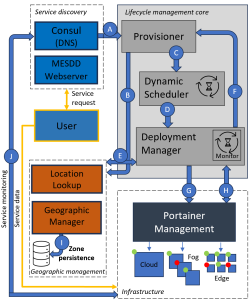
Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation Special Issue on
Multimodal Learning for Visual Intelligence: From Emerging Techniques to Real-World Applications
In recent years, the integration of vision with complementary modalities such as language, audio, and sensor signals has emerged as a key enabler for intelligent systems that operate in unstructured environments. The emergence of foundation models and cross-modal pretraining has brought a paradigm shift to the field, making it timely to revisit the core challenges and innovative techniques in multimodal visual understanding.
This Special Issue aims to collect cutting-edge research and engineering practices that advance the understanding and development of visual intelligence systems through multimodal learning. The focus is on the deep integration of visual information with complementary modalities such as text, audio, and sensor data, enabling more comprehensive perception and reasoning in real-world environments. We encourage contributions from both academia and industry that address current challenges and propose novel methodologies for multimodal visual understanding.
Topics of interest include, but are not limited to:
- Multimodal data alignment and fusion strategies with a focus on visual-centric modalities
- Foundation models for multimodal visual representation learning
- Generation and reconstruction techniques in visually grounded multimodal scenarios
- Spatiotemporal modeling and relational reasoning of visual-centric multimodal data
- Lightweight multimodal visual models for resource-constrained environments
- Key technologies for visual-language retrieval and dialogue systems
- Applications of multimodal visual computing in healthcare, transportation, robotics, and surveillance
Guest editors:
Guanghui Yue, PhD
Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
Email: yueguanghui@szu.edu.cn
Weide Liu, PhD
Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA
Emai: weide001@e.ntu.edu.sg
Ziyang Wang, PhD
The Alan Turing Institute, London, UK
Emai: zwang@turing.ac.uk
Hadi Amirpour, PhD
Alpen-Adria University, Klagenfurt, Austria
Emai: hadi.amirpour@aau.at
Zhedong Zheng, PhD
University of Macau, Macau, China
Email: zhedongzheng@um.edu.mo
Wei Zhou, PhD
Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK
Email: zhouw26@cardiff.ac.uk
Timeline:
Submission Open Date 30/05/2025
Final Manuscript Submission Deadline 30/11/2025
Editorial Acceptance Deadline 30/05/2026
Keywords: Multimodal Learning, Visual-Language Models, Cross-Modal Pretraining, Multimodal Fusion and Alignment, Spatiotemporal Reasoning, Lightweight Multimodal Models, Applications in Healthcare and Robotics