2022 IEEE/ACM 2nd Workshop on Distributed Machine Learning for the Intelligent Computing Continuum (DML-ICC) In conjuction with IEEE/ACM UCC 2022 December 6-9, 2022 | Vancouver, Washington, USA
Authors: Narges Mehran (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt) and Radu Prodan (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt)
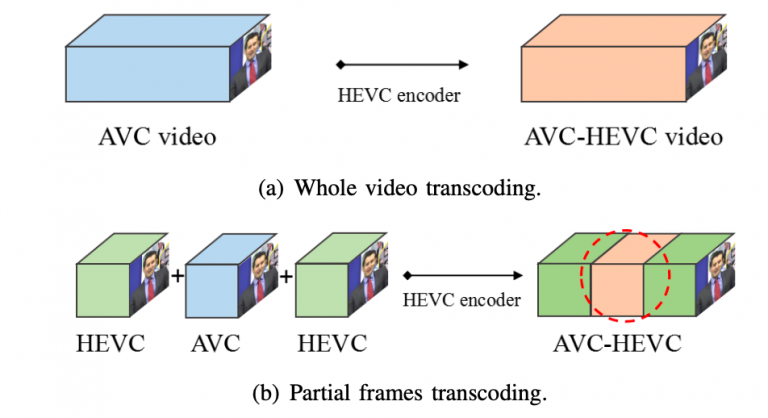
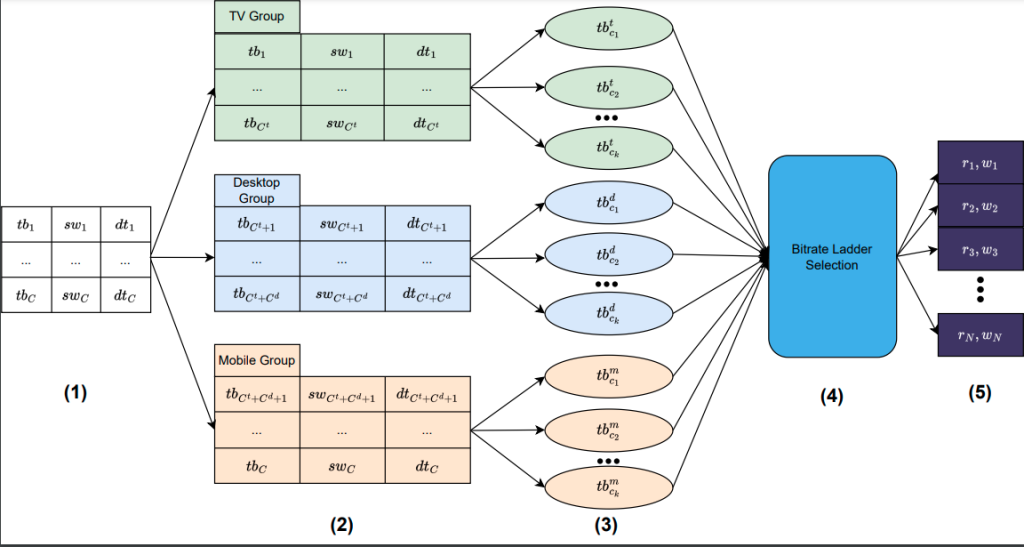
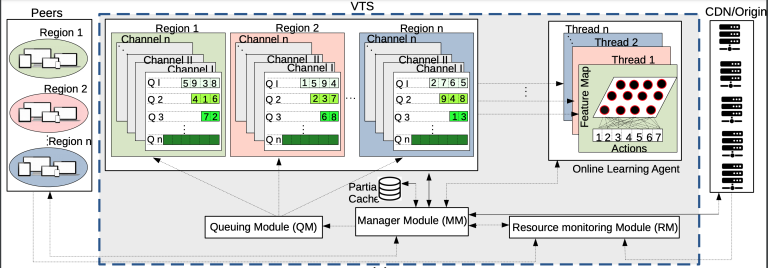
Abstract: Processing rapidly growing data encompasses complex workflows that utilize the Cloud for high-performance computing and the Fog and Edge devices for low-latency communication. For example, autonomous driving applications require inspection, recognition, and classification of road signs for safety inspection assessments, especially on crowded roads. Such applications are among the famous research and industrial exploration topics in computer vision and machine learning. In this work, we design a road sign inspection workflow consisting of 1) encoding and framing tasks of video streams captured by camera sensors embedded in the vehicles, and 2) convolutional neural network (CNN) training and inference models for accurate visual object recognition. We explore a matching theoretic algorithm named CODA [1] to place the workflow on the computing continuum, targeting the workflow processing time, data transfer intensity, and energy consumption as objectives. Evaluation results on a real computing continuum testbed federated among four Cloud, Fog, and Edge providers reveal that CODA achieves 50%-60% lower completion time, 33%-59% lower CO2 emissions, and 19%-45% lower data transfer intensity compared to two stateof-the-art methods.




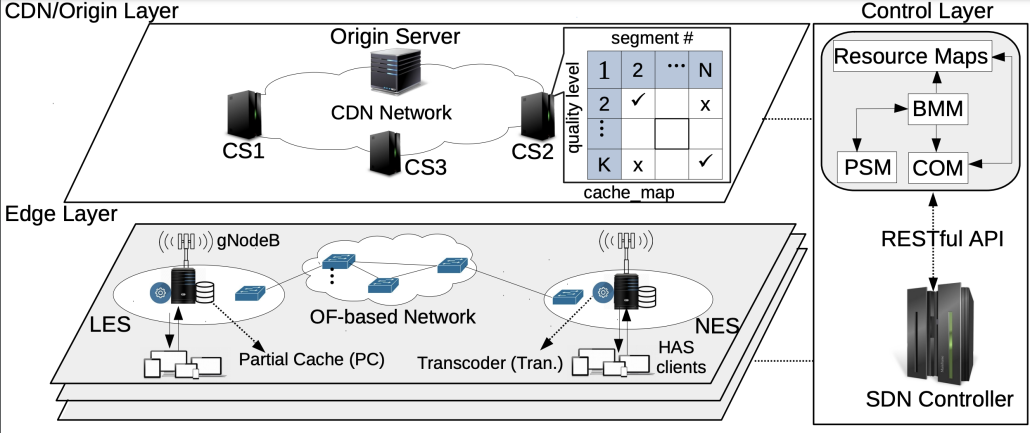



 During the period Aug 1st –26th, 2022, Hamza Baniata, a PhD Candidate at the Department of Computer Science, University of Szeged, Hungary, has visited the institute of Information Technology of the University of Klagenfurt, Austria. Under the collaborative supervision by Prof.
During the period Aug 1st –26th, 2022, Hamza Baniata, a PhD Candidate at the Department of Computer Science, University of Szeged, Hungary, has visited the institute of Information Technology of the University of Klagenfurt, Austria. Under the collaborative supervision by Prof.