Machine Learning-Based Decoding Energy Modeling for VVC Streaming
2025 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)
14-17 September, Anchorage, Alaska, USA
https://2025.ieeeicip.org/
Reza Farahani (AAU Klagenfurt, Austria), Vignesh V Menon (Fraunhofer HHI, Germany), and Christian Timmerer (AAU Klagenfurt, Austria)
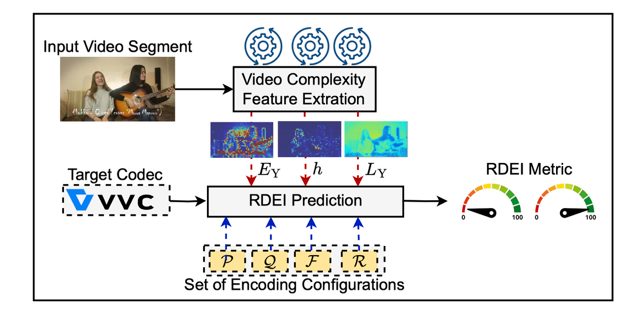
Abstract: Efficient video streaming requires jointly optimizing encoding parameters (bitrate, resolution, compression efficiency) and decoding constraints (computational load, energy consumption) to balance quality and power efficiency, particularly for resource-constrained devices. However, hardware heterogeneity, including differences in CPU/GPU architectures, thermal management, and dynamic power scaling, makes absolute energy models unreliable, particularly for predicting decoding consumption. This paper introduces the Relative Decoding Energy Index (RDEI), a metric that normalizes decoding energy consumption against a baseline encoding configuration, eliminating device-specific dependencies to enable cross-platform comparability and guide energy-efficient streaming adaptations. We use a dataset of 1000 video sequences to extract complexity features capturing spatial and temporal variations, employ Versatile Video Coding (VVC) open-source toolchain using VVenC/VVdeC with various resolutions, framerate, encoding preset and quantization parameter (QP) sets, and model RDEI using Random Forest (RF), XGBoost, Linear Regression (LR), and Shallow Neural Networks (NN) for decoding energy prediction. Experimental results demonstrate that RDEI-based predictions provide accurate decoding energy estimates across different hardware, ensuring cross-device comparability in VVC streaming.
Keywords: Video Streaming; Energy Prediction; Versatile Video Coding (VVC); Video Complexity Analysis.